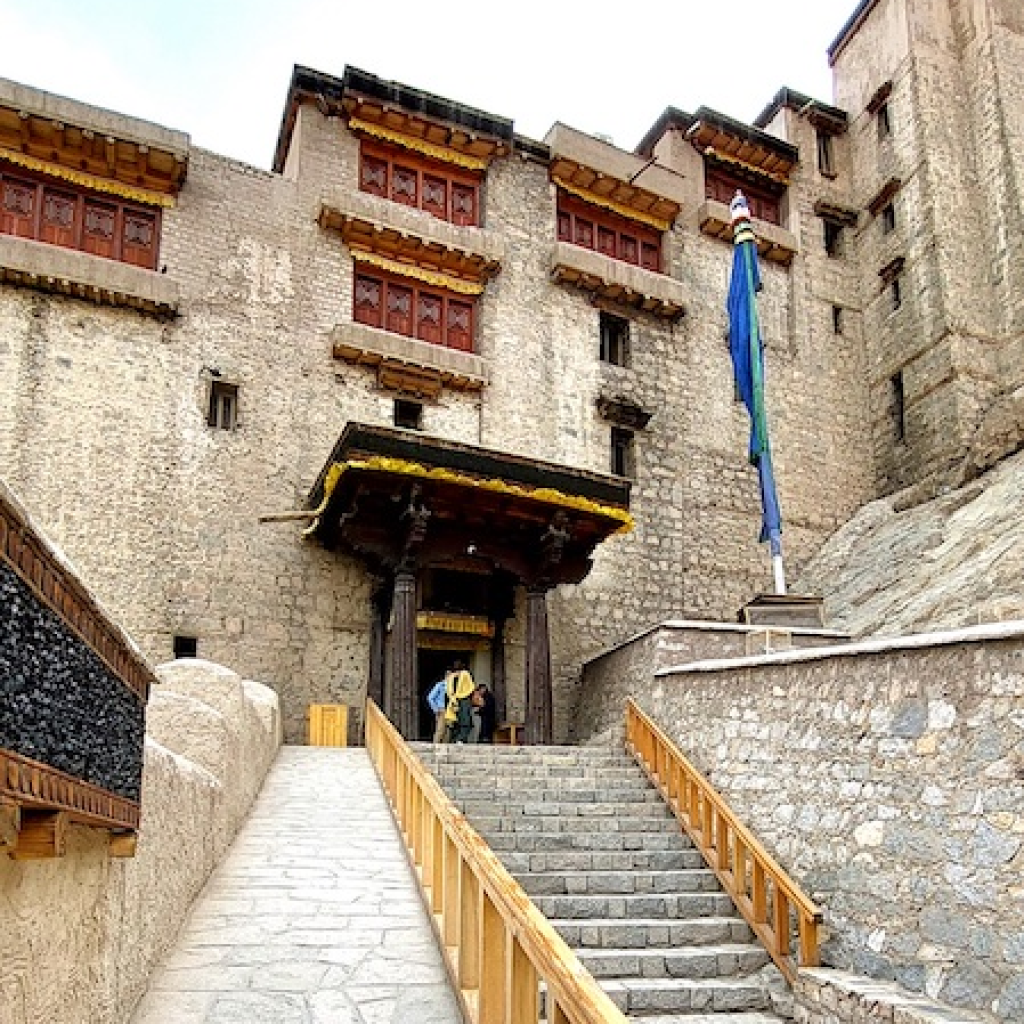
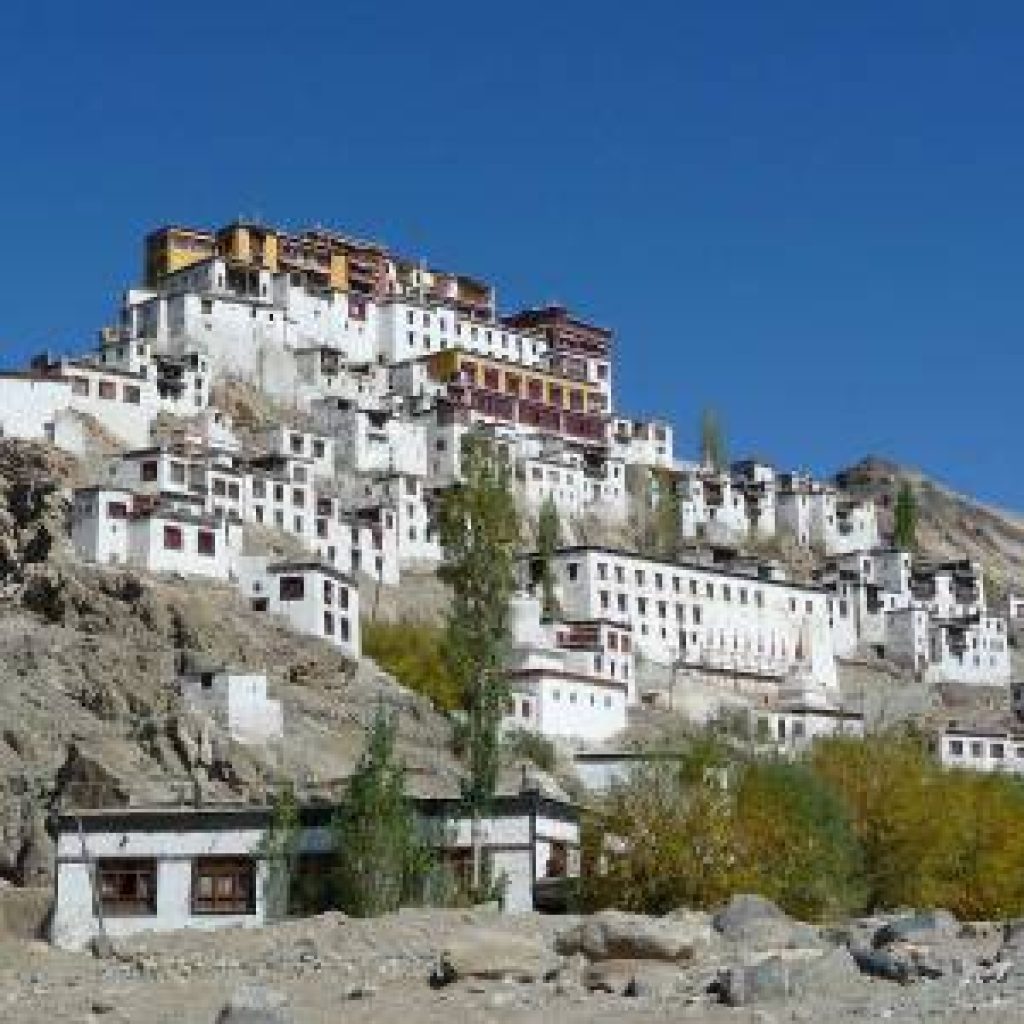
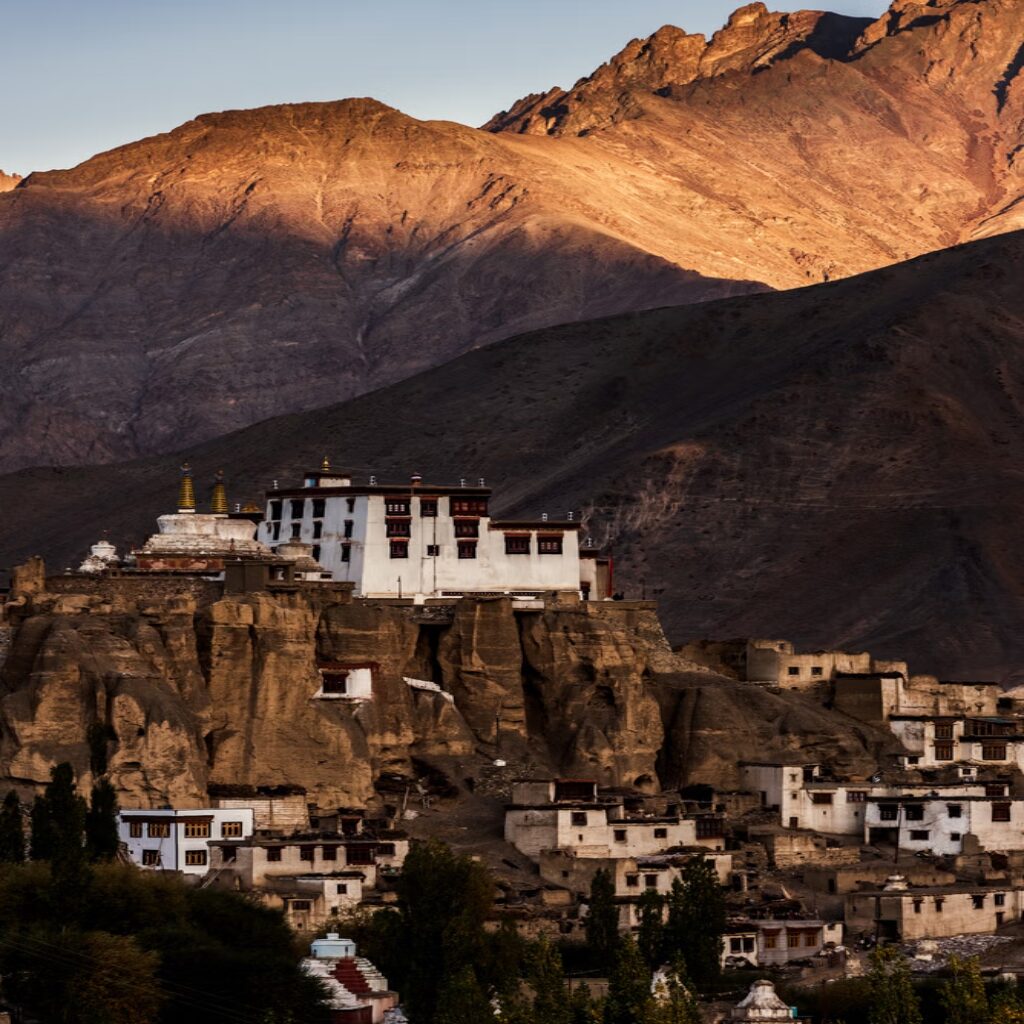
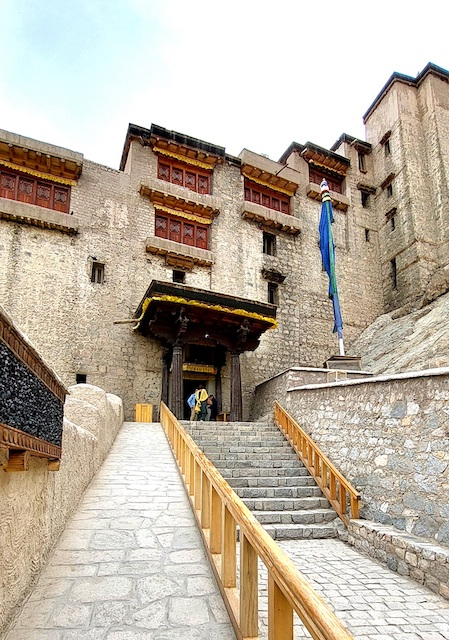
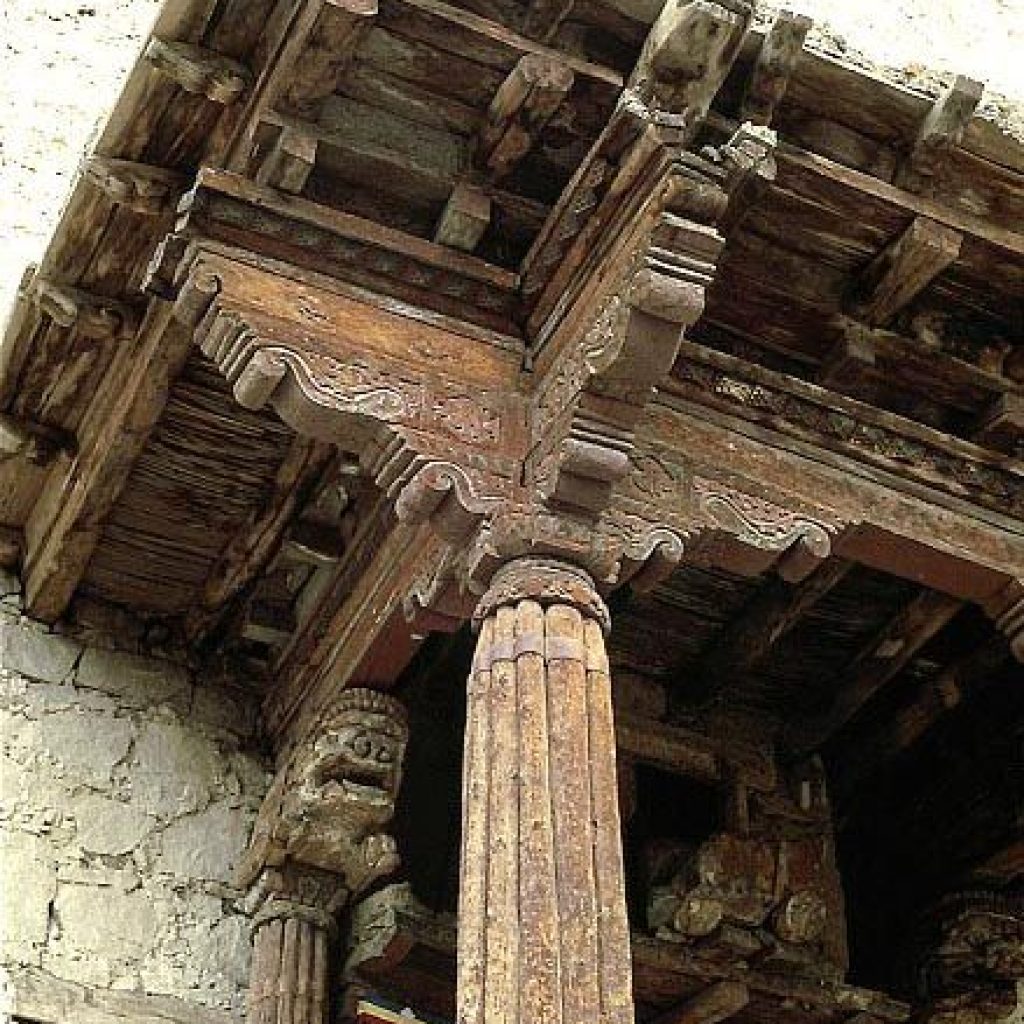
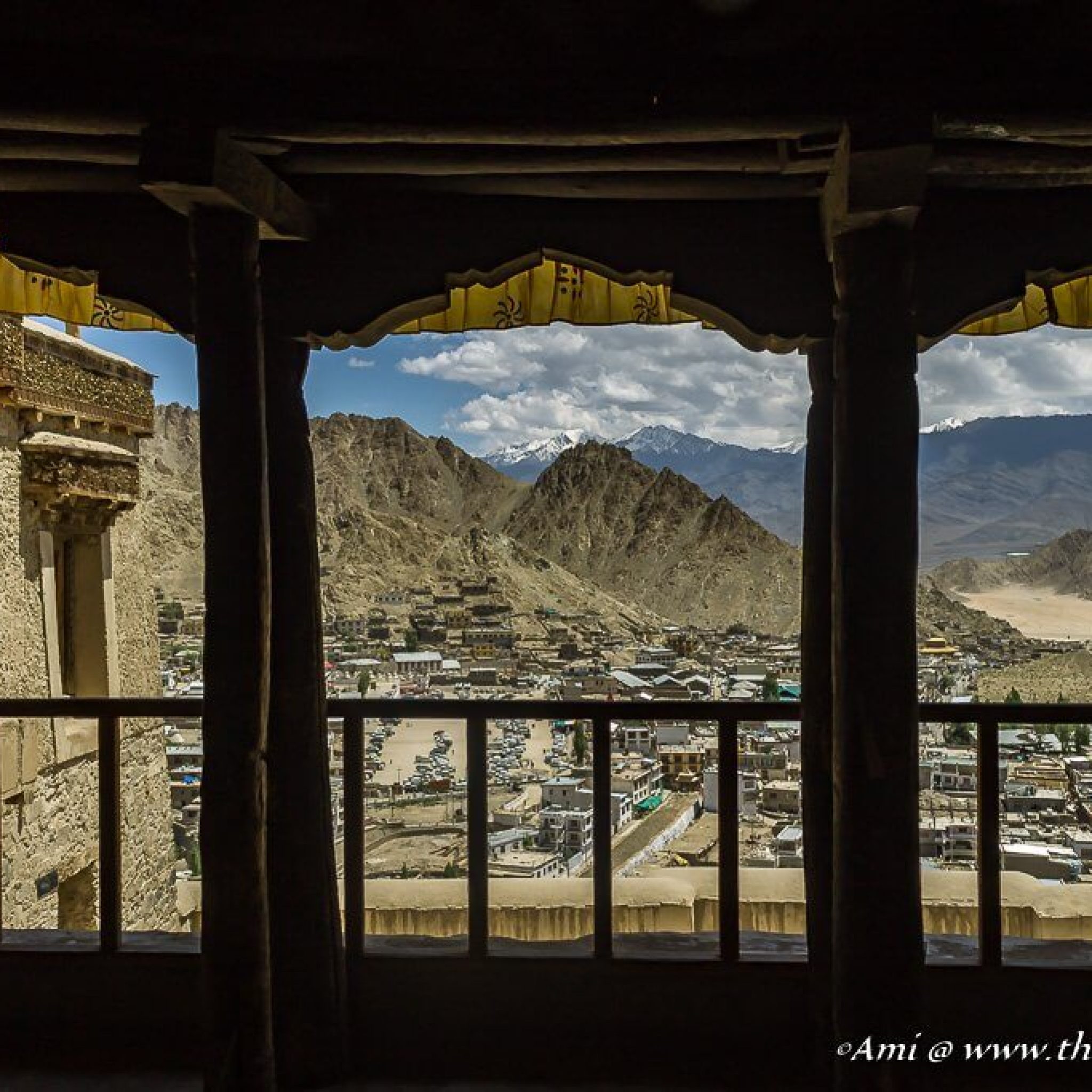
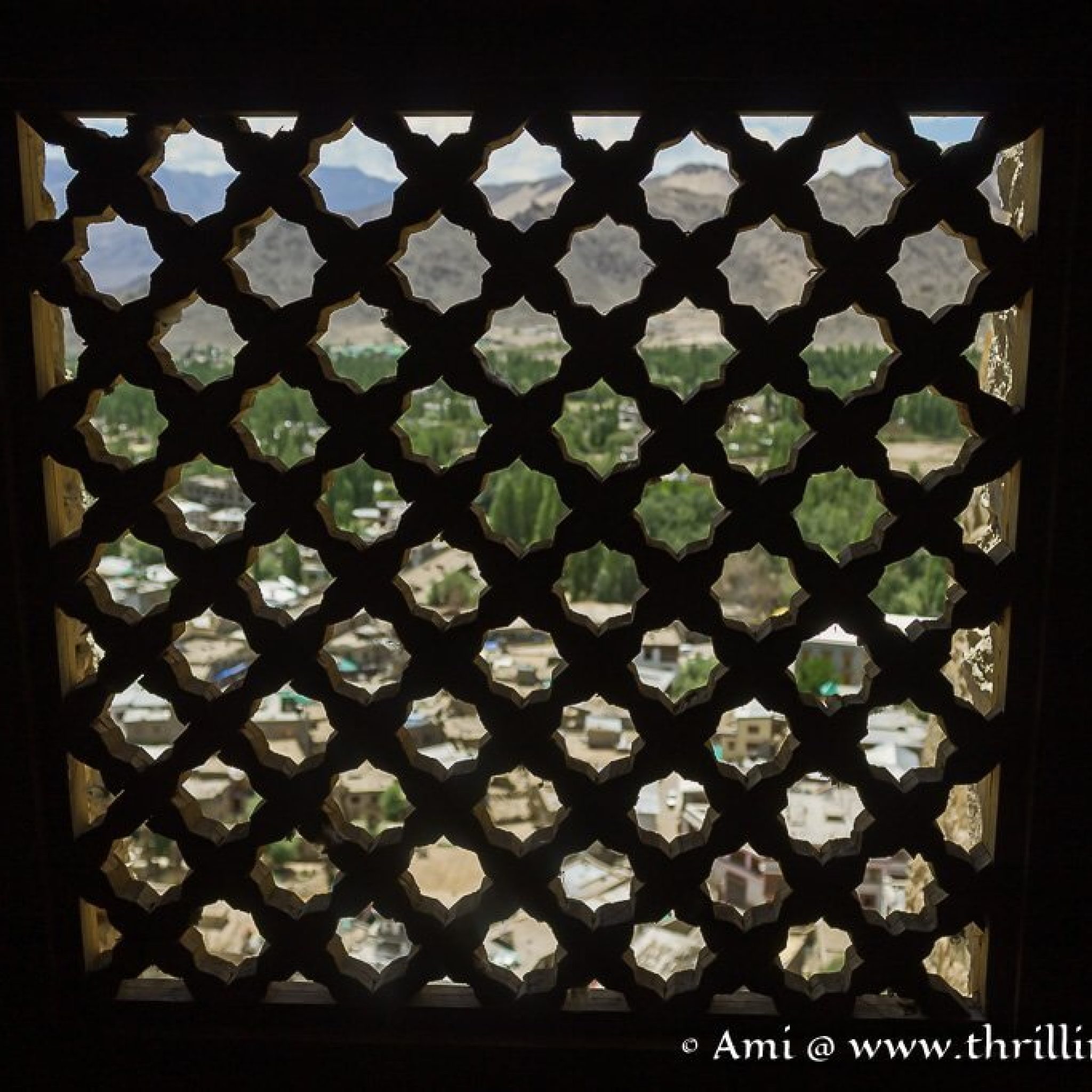
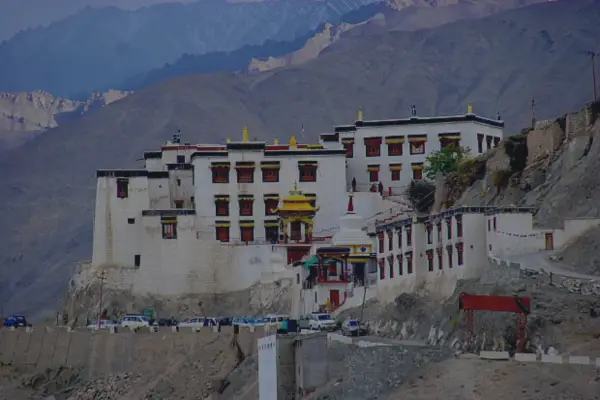
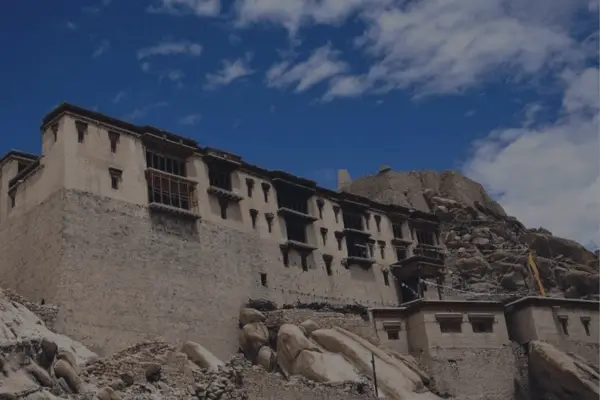
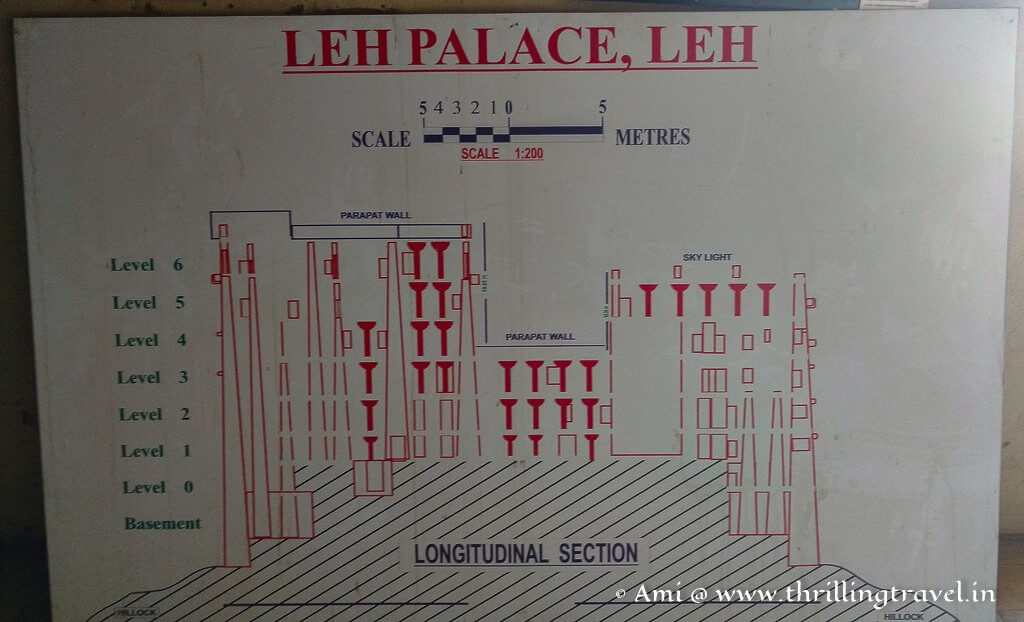
Matho Monastery was established around 1410 CE by Lama Dugpa Dorje, a Tibetan Buddhist monk who brought the Sakya tradition to Ladakh. This school of Buddhism, which originated in Tibet in the 11th century, is characterized by a blend of monastic discipline and tantric practices, creating a deeply esoteric spiritual path.
Over the centuries, Matho served as an important center for Sakya scholarship and meditation in Ladakh, especially during times when cross-border exchanges with Tibet were more common. Despite its smaller size and quieter presence compared to monasteries like Hemis or Thiksey, Matho has managed to preserve its distinct identity and rituals, especially through its unique oracle tradition.
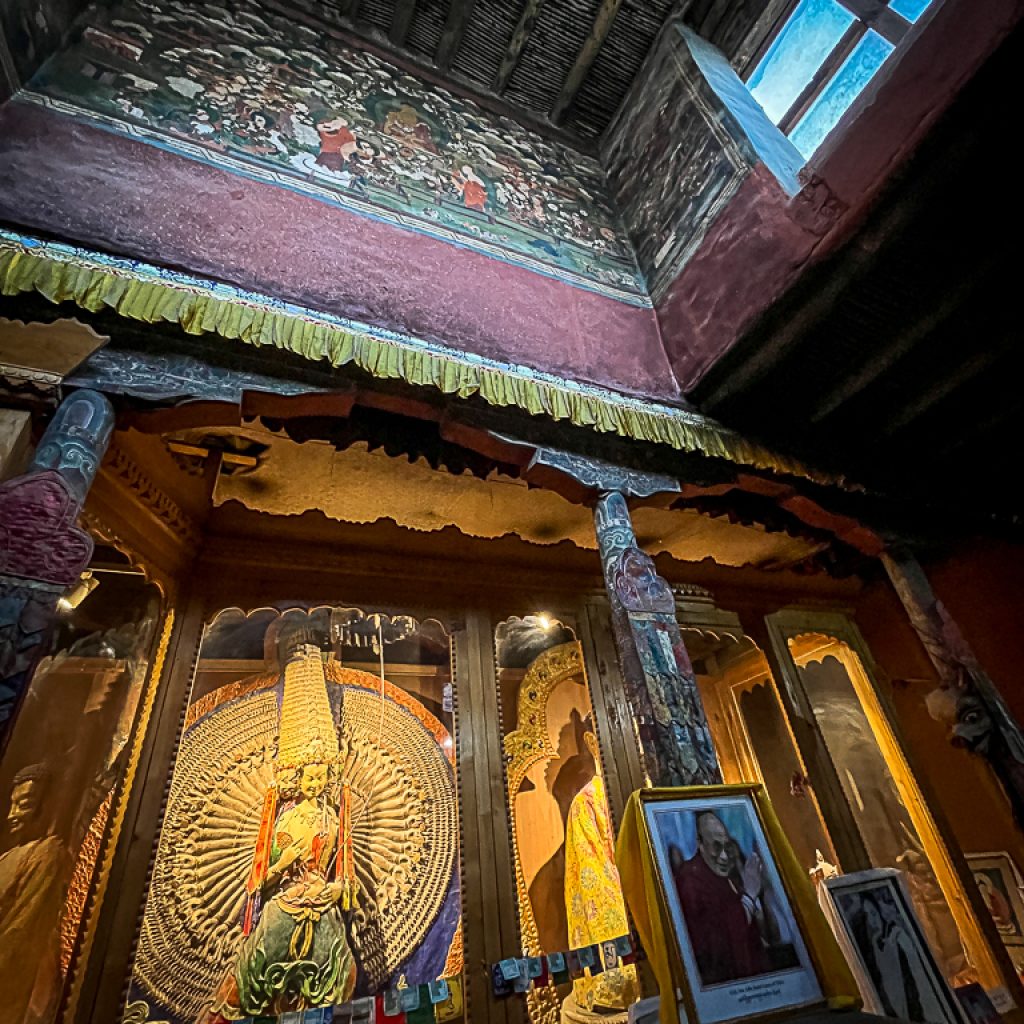
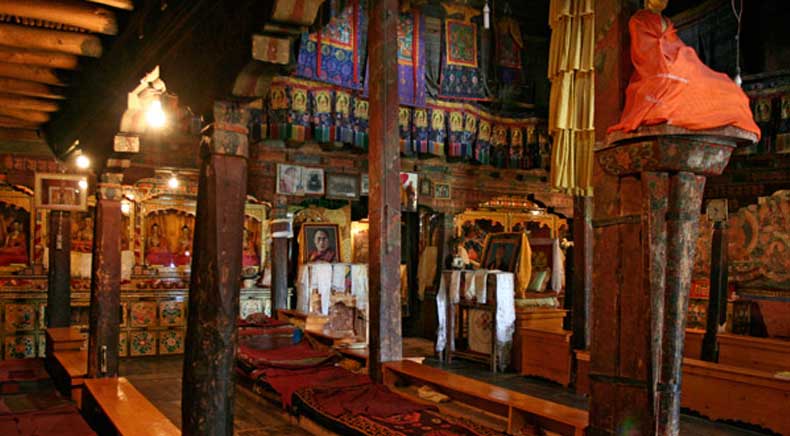
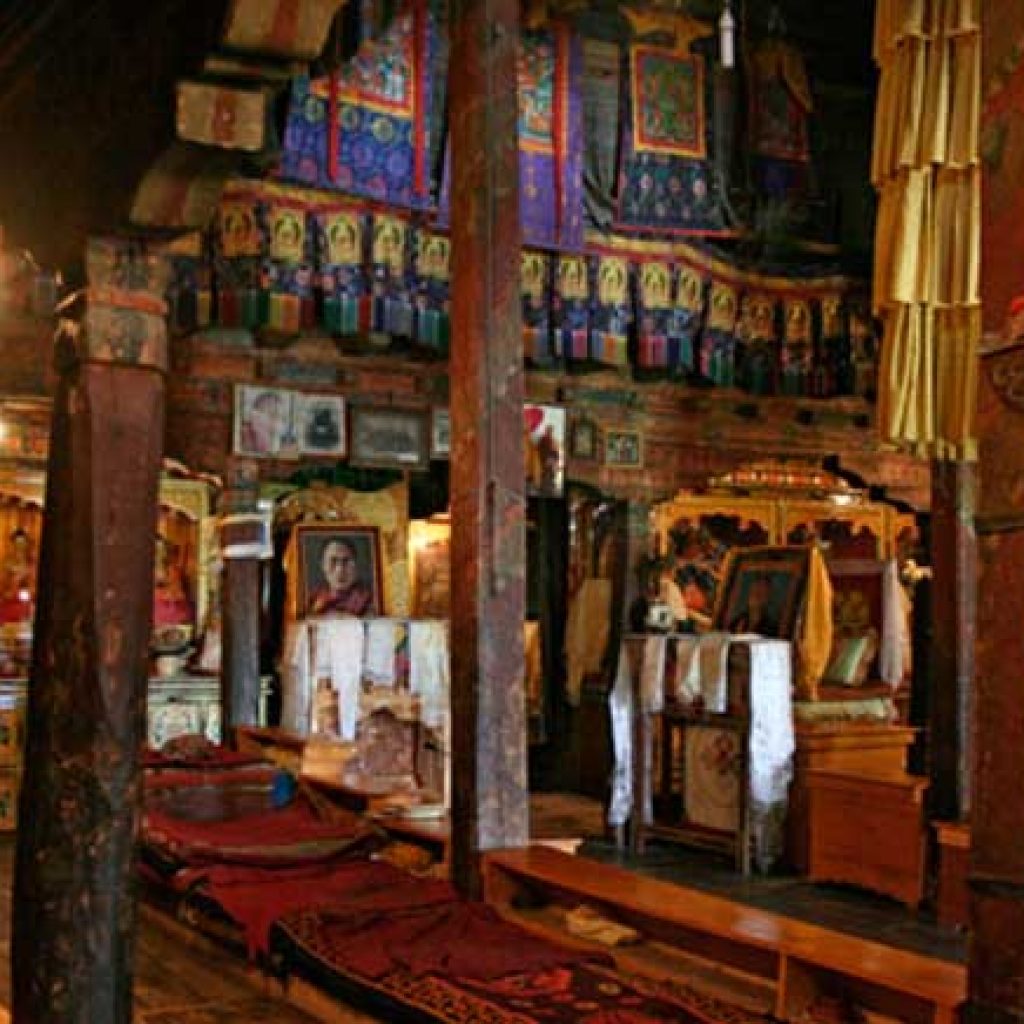
The monastery is also known for housing a collection of ancient thangkas, scriptures, and ritual instruments, many of which are used only during special ceremonies.